이 문서를 언급한 문서들2
Providing DOM API to Worker Threads
Objective
- Provide synchronous DOM API Access to Web Worker Threads
- Part of Brane
Start
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<script>
const myWorker = new Worker('worker.js')
myWorker.onmessage = function (e) {
console.log(`Worker said : ${e.data}`)
}
function msg() {
myWorker.postMessage('MAIN')
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello</h1>
<button id="btn" onclick="msg()">Communicate with worker</button>
</body>
</html>
postMessage('Worker is ready!')
onmessage = function (e) {
console.log('WORKER.onMessage:', e.data)
postMessage(`I am a worker. Hello, ${e.data}.`)
}
The type of e is MessageEvent.
MessageEvent - Web APIs.
Synchronous Call from Main
To enable SharedArrayBuffer, we need a secure context crossOriginIsolated.
crossOriginIsolated is false.
To set crossOriginIsolated to true, we need two headers.
- Cross-Origin Opener Policy.
same-origin - Cross-Origin Embedder Policy.
require-corp
Tim already built a super easy toolkit that sets both headers to the desired values. Then we only need to
npx serve-isolated .- braneproject/serve-isolated: Serve static contents under the
crossOriginIsolatedmode.
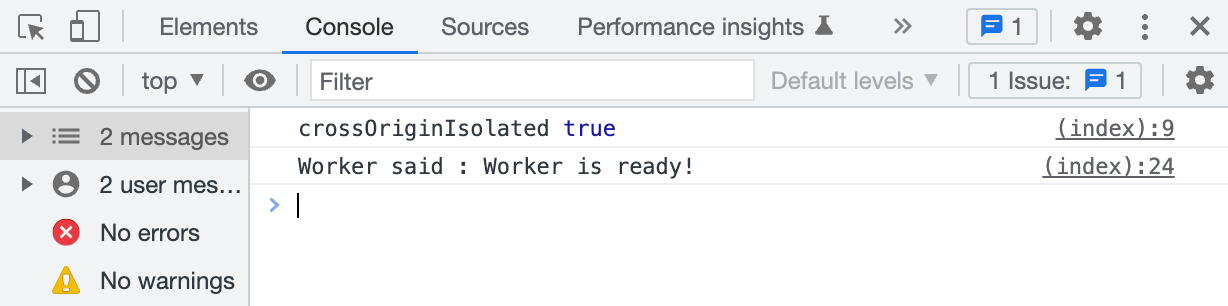
This is so cool.
Save Point 1
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<script>
console.log('crossOriginIsolated', crossOriginIsolated)
// defining SAB and sending it to the worker
const sab = new SharedArrayBuffer(1024)
const int32 = new Int32Array(sab)
const myWorker = new Worker('worker.js')
function syncSab() {
myWorker.postMessage({
type: 'init',
sab: sab,
})
}
myWorker.onmessage = function (e) {
console.log(`Worker said : ${e.data}`)
}
function increment() {
// ↓ Same as int32[0]++, but Thread Safe
Atomics.add(int32, 0, 1)
Atomics.notify(int32, 0)
}
function freeze() {
// Sets [0] to 0.
// the heartbeat function waits if [0] is 0.
Atomics.store(int32, 0, 0)
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>RPC Demo</h1>
<button id="syncSab" onclick="syncSab()">Send SAB to Worker</button>
<button id="increment" onclick="increment()">Increment</button>
<button id="freeze" onclick="freeze()">Freeze</button>
</body>
</html>
postMessage('Worker is ready!')
let sab = undefined
let int32 = undefined
onmessage = function (e) {
console.log('WORKER.onMessage:', e.data)
if (e.data?.type === 'init') {
sab = e.data.sab
int32 = new Int32Array(sab)
console.log('Received SAB')
Atomics.wait(int32, 0, 0)
heartbeat()
}
postMessage(`I am a worker. Hello, ${JSON.stringify(e.data)}.`)
}
function heartbeat() {
setInterval(() => {
Atomics.wait(int32, 0, 0) // doesn't beat if [0] is 0
console.log('WORKER.heartbeat:', Atomics.load(int32, 0))
Atomics.add(int32, 0, 1)
}, 1000)
}
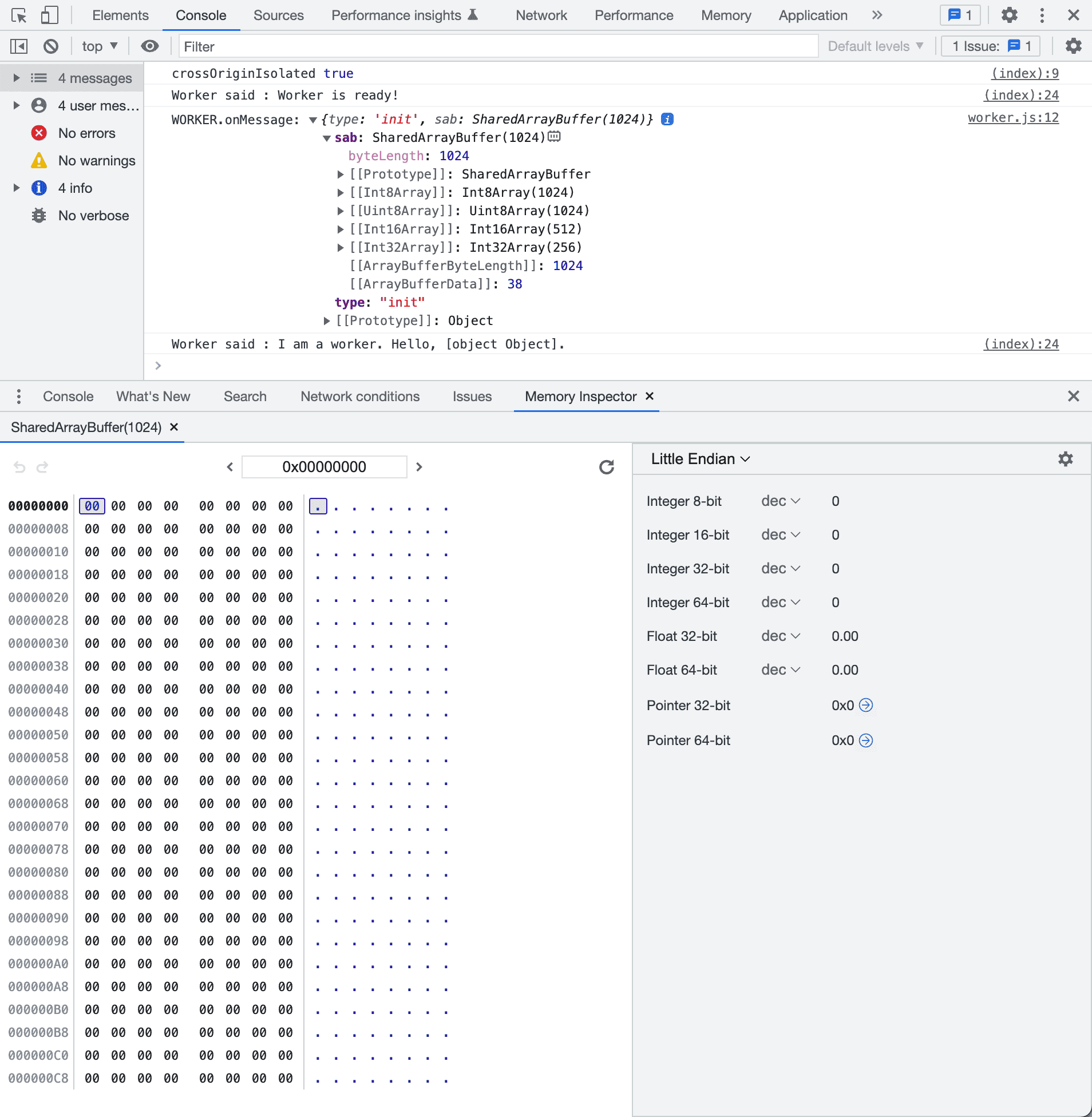
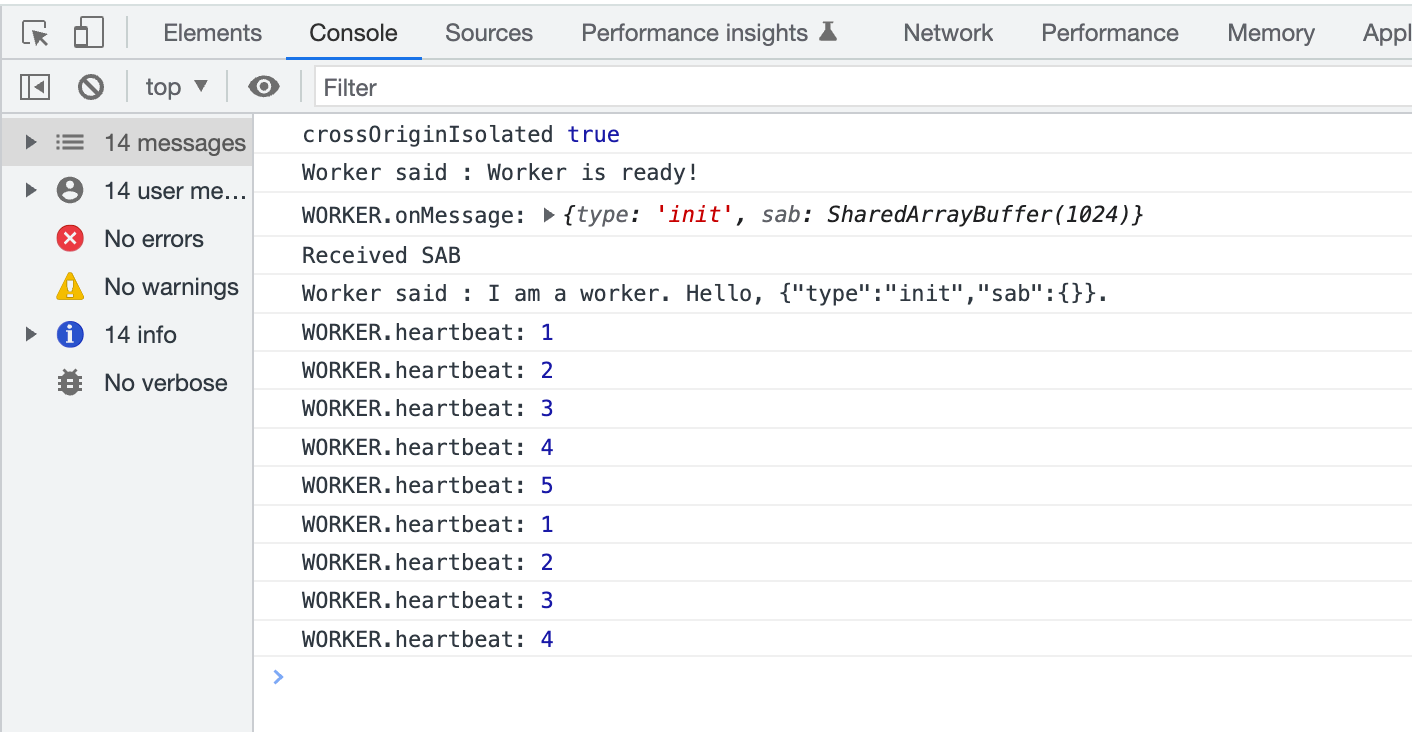
- Sends SAB when clicking the Send SAB to Worker button.
[0]is set to zero, so the heartbeat function waits.
- If Increment button is clicked, SAB
[0]is no longer 0.- We then notify any function waiting at
[0].
- We then notify any function waiting at
heartstarts beating, incrementing SAB[0].
Remote Procedure Call
- See Remote procedure call
- RPC is a request-response protocol. An RPC is initiated by the client, which sends a request message to a known remote server to execute a specified procedure with supplied parameters. The remote server sends a response to the client, and the application continues its process. While the server is processing the call, the client is blocked (it waits until the server has finished processing before resuming execution) unless the client sends an asynchronous request to the server, such as an XMLHttpRequest.
Note that
mainonlynotify().mainneverwait().workerwill yield towait().
Complete
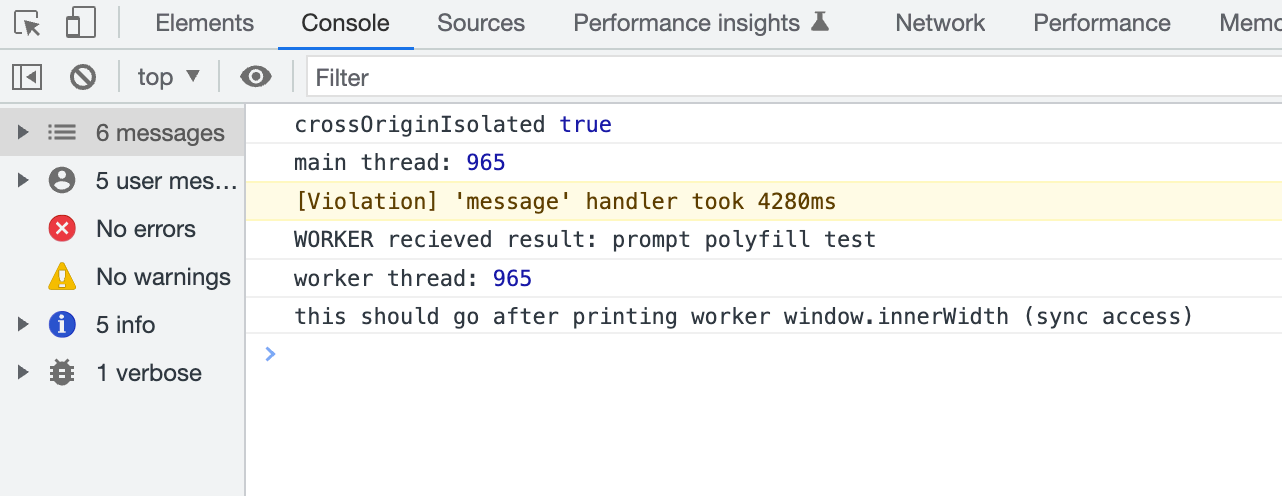
Voila! I have created a synchronous polyfill layer for window.prompt and window.innerHeight functions inside a worker.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<script src="./status.js"></script>
<title>Worker RPC/title>
<script>
console.log('crossOriginIsolated', crossOriginIsolated)
const Status = {
UNINITIALISED: 0,
READY: 1,
COMPLETED: 2,
ERROR: 3,
}
const worker = new Worker('worker.js')
worker.onmessage = function (e) {
const message = e.data
if (message?.func === 'prompt') {
const sab = message?.sharedArrayBuffer
const int32 = new Int32Array(sab)
const ans = prompt(message?.msg)
if (ans) {
const enc = new TextEncoder()
const buf = enc.encode(ans)
int32.set(buf, 0)
Atomics.notify(int32, 0, 1)
}
} else if (message?.func === 'windowInnerWidth') {
const sab = message?.sharedArrayBuffer
const int32 = new Int32Array(sab)
int32.set([window.innerWidth], 0)
Atomics.notify(int32, 0, 1)
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Worker RPC Demo</h1>
<button onclick="console.log('hello')">Console Log</button>
<button onclick="console.log('main thread:', window.innerWidth)">
Console Log Window Inner Width
</button>
</body>
</html>
const Status = {
UNINITIALISED: 0,
READY: 1,
COMPLETED: 2,
ERROR: 3,
}
function sleep(ms) {
const end = Date.now() + ms
while (Date.now() < end) {}
return Date.now()
}
// polyfill layer for Worker.Prompt
function prompt(msg) {
const sab = new SharedArrayBuffer(1024)
const int32 = new Int32Array(sab)
Atomics.store(int32, 0, Status.READY)
postMessage({
sharedArrayBuffer: sab,
func: 'prompt',
msg: msg,
})
// Waiting
Atomics.wait(int32, 0, Status.READY)
// Waiting complete, get the result
const ab = new ArrayBuffer(sab.byteLength)
const view = new Uint8Array(ab)
view.set(new Uint8Array(sab))
const decoder = new TextDecoder()
const string = decoder.decode(view)
console.log('WORKER recieved result:', string)
}
const window = {
get innerWidth() {
const sab = new SharedArrayBuffer(4)
const int32 = new Int32Array(sab)
Atomics.store(int32, 0, Status.READY)
postMessage({
sharedArrayBuffer: sab,
func: 'windowInnerWidth',
})
Atomics.wait(int32, 0, Status.READY)
const innerWidth = Atomics.load(int32, 0)
return innerWidth
},
}
// Therefore we can...
sleep(5000)
prompt('hello!')
sleep(2000)
console.log('worker thread:', window.innerWidth)
console.log('this should go after printing worker window.innerWidth (sync access)')
// This all happens synchronously in multi-thread.