Links to This Note16
- blank=True vs null=True in Django... absence of a value as Python `None`.
- Scala... almost ten times faster than Python because it relies on the ...
- Render.com... languages such as Ruby, PHP, Python, Node, and Java.
- Real Exams... Get Job Done SQL, React, Python
- PythonYou can offset with Python's `enumerate` function with list splitting.
- Person 1E6ABA... as possible, whereas the Tensorflow Python team wanted to make everything ...
- Migrating Project Aldehyde to FlightControl (February 24誠鉉)... a jankily frankensteined pipe of Python and Node to generate my ...
- Mathematics under The Library of Babel- I tried making a Python script to backtrack the combinations.
- Higher-Level Languages and Their Speeds- Python
- Heap (Computer Systems)On the other hand, Java, Python, or other higher-level languages use ...
- Grammarly Work Note 2023-06-07Functions are either in Python or Scala
- Get Job Done... - Building Python Data Parser
- Daniele Romanini et al. PyVertical- PyVertical is a Python framework that utilizes SplitNNs and ...
- Coding Tests- Will use Python (main language) and C++ (supplementary ...
- 1046 Last Stone Weight- Space: $O(1)$ in Python
- 0001 Two SumI used Python Dictionary to store complementing values. ...
Python
tip
Special thanks to Ishu Agrawal
Heap
Heaps are complete binary trees where the value of each node must be no greater than (or less than) the value of its child nodes.
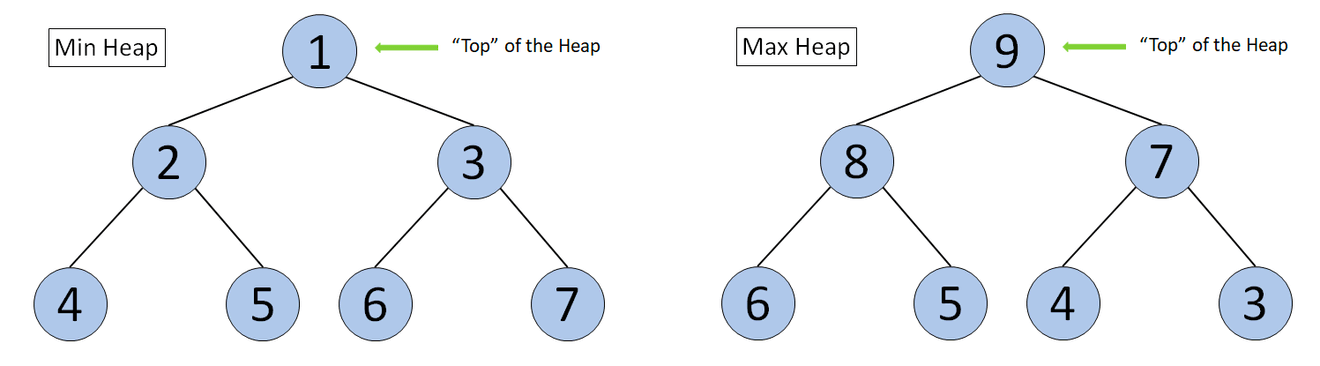
- Python only supports Min Heaps
import heapqheapq.heapify(arr)heapq.heappop(arr)heapq.heappush(arr, x)heapq.nsmallest(k, arr, key=func)returns a list with theksmallest elements in the iterablearrbased on a comparator functionfunc- Runtime:
heapq.nlargest(k, arr, key=func)returns a list with theklargest elements in the iterablearrbased on a comparator functionfunc- Runtime:
| Operation | Runtime |
|---|---|
| Find min/max | |
| Search | |
| Insert | |
| Remove | |
| Heapify Array |
List Offsetting
You can offset with Python's enumerate function with list splitting.
enumerate(nums[offset::])
Dictionary
Alphanumeric Testing
c.isalnum()
Making 2d Arrays
- using
visited = [[False] * len(image[0])] * len(image)will not work- the rows will share the same memory and change in one will reflect on the others
- use
arr = [[0 for i in range(cols)] for j in range(rows)]